
Experience the power of Tetracycline and Doxycycline to combat bacterial infections with unmatched effectiveness. The resistance properties of these antibiotics make them the top choice for treating a wide range of infections.
Description of Tetracycline
Tetracycline is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that is commonly used to treat a variety of bacterial infections. It belongs to the class of tetracycline antibiotics and works by inhibiting the growth of bacteria. Tetracycline is effective against a wide range of bacteria, including both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. It is commonly prescribed for infections such as acne, urinary tract infections, respiratory tract infections, and sexually transmitted diseases. Tetracycline is available in oral and topical forms, making it convenient for different types of infections.
| Drug Class | Tetracycline Antibiotic |
| Mechanism of Action | Inhibition of bacterial protein synthesis |
| Common Uses | Acne, urinary tract infections, respiratory infections |
| Administration | Oral, Topical |
Benefits of Tetracycline
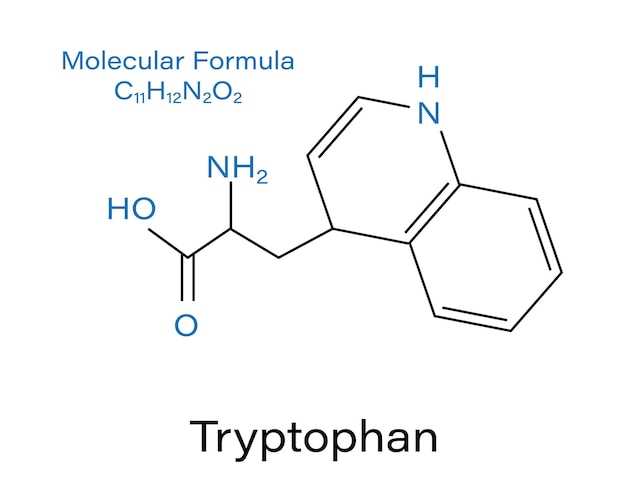
Tetracycline is a powerful antibiotic that is widely used to treat a variety of bacterial infections. It belongs to a class of antibiotics called tetracyclines, which work by inhibiting the growth and spread of bacteria in the body. Tetracycline is effective against a wide range of bacteria, making it a versatile and important medication in the fight against infections.
One of the key benefits of tetracycline is its ability to treat both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. This broad spectrum of activity means that tetracycline can be used to combat a wide range of infections, from acne to urinary tract infections to respiratory tract infections. This versatility makes tetracycline a valuable tool for healthcare providers in treating a variety of bacterial illnesses.
Key benefits of tetracycline include:
- Effective Treatment: Tetracycline is effective against a wide range of bacterial infections, making it a versatile treatment option.
- Low Side Effects: Tetracycline is generally well-tolerated by most patients and has fewer side effects compared to other antibiotics.
Overall, tetracycline is an important antibiotic with a range of benefits that make it a valuable tool in the fight against bacterial infections.
Benefits of Tetracycline
Tetracycline is a versatile antibiotic that offers numerous benefits in treating various bacterial infections. It is effective against a wide range of pathogens, making it a versatile option for both common and serious infections.
One of the key advantages of tetracycline is its ability to penetrate different tissues in the body, allowing it to effectively target bacteria that are responsible for causing infections. This makes it a valuable tool in combating a variety of infections, from skin and respiratory infections to urinary tract and sexually transmitted diseases.
Additionally, tetracycline is well-tolerated by most individuals, with minimal side effects compared to other antibiotics. This makes it a popular choice for treating both adults and children, as it allows for effective treatment of bacterial infections without significant adverse reactions.
Furthermore, tetracycline is available in multiple formulations, including capsules, tablets, and liquids, making it convenient for patients with different preferences and needs. Its long history of use and proven effectiveness make tetracycline a reliable option for healthcare providers looking to successfully manage bacterial infections.
Effective Treatment
Tetracycline is a highly effective treatment for a wide range of bacterial infections. It works by inhibiting the growth of bacteria and stopping their ability to replicate. This makes it a powerful tool in fighting infections and restoring health.
When used as directed by a healthcare professional, tetracycline can effectively treat various conditions, including acne, urinary tract infections, respiratory infections, and certain sexually transmitted diseases.
Its broad-spectrum activity makes it a versatile option for many different types of infections, offering relief to patients and helping them recover quickly.
Low Side Effects
One of the key advantages of tetracycline antibiotics like doxycycline is their low incidence of side effects. Unlike some other antibiotics that can cause a range of adverse reactions, tetracyclines are generally well-tolerated by most patients.
The most common side effects associated with tetracycline use include gastrointestinal upset, such as nausea or vomiting, and photosensitivity, which can cause skin reactions when exposed to sunlight. However, these side effects are usually mild and temporary, and most patients are able to continue their treatment without significant discomfort.
Overall, the low incidence of side effects makes tetracycline antibiotics a preferred choice for many healthcare providers when treating a variety of bacterial infections.
Addressing Resistance Issues
Understanding and addressing resistance mechanisms is crucial in the fight against antibiotic resistance. Tetracycline and doxycycline are no exception. Researchers are actively studying the mechanisms behind resistance to these antibiotics to develop effective strategies for combating them.
Research on Resistance Mechanisms
Scientists are investigating how bacteria develop resistance to tetracycline and doxycycline. One common mechanism is the production of efflux pumps that actively remove the antibiotics from the bacterial cell. Other mechanisms include the modification of target sites and the inactivation of the antibiotics. By understanding these mechanisms, researchers can develop new drugs or combination therapies to prevent or overcome resistance.
| Resistance Mechanism | Description |
|---|---|
| Efflux Pumps | Bacterial cells pump out antibiotics, reducing their concentration inside the cell. |
| Target Site Modification | Bacteria alter the target sites of antibiotics, making them less effective. |
| Inactivation | Bacteria produce enzymes that inactivate the antibiotics, rendering them ineffective. |
By focusing on these resistance mechanisms, researchers can develop innovative solutions to combat resistance, ensuring the continued efficacy of tetracycline and doxycycline in treating bacterial infections.
Research on Resistance Mechanisms
Research on resistance mechanisms is crucial for understanding how bacteria develop resistance to antibiotics like doxycycline. Scientists study how bacteria mutate and acquire genes that make them resistant to the effects of antibiotics. By understanding these mechanisms, researchers can develop new strategies to combat antibiotic resistance and improve the effectiveness of treatments.
| Types of Resistance Mechanisms | Description |
| 1. Efflux Pumps | Some bacteria use efflux pumps to remove antibiotics from their cells, reducing the concentration of the drug and rendering it ineffective. |
| 2. Target Modification | Bacteria can modify the target site of antibiotics, making them unable to bind and exert their antimicrobial effects. |
| 3. Enzymatic Inactivation | Some bacteria produce enzymes that can inactivate antibiotics, preventing them from killing the bacteria. |
By studying these resistance mechanisms, researchers can develop new drugs that are less susceptible to resistance mechanisms or combine multiple drugs to overcome resistance. Continued research in this area is essential to ensuring the continued efficacy of antibiotic treatments.
Strategies for Combating Resistance
Drug resistance is a significant concern in the medical field, particularly with antibiotics like Tetracycline. To combat resistance effectively, several strategies can be employed:
1. Combination Therapy:
Using Tetracycline in combination with other antibiotics can help prevent resistance by targeting different mechanisms of action in bacteria. This approach reduces the likelihood of microbial adaptation and development of resistance.
2. Proper Antibiotic Use:
It is crucial to use Tetracycline and other antibiotics properly to reduce the emergence of resistance. This includes following prescribed dosages, completing the full course of treatment, and avoiding unnecessary or inappropriate antibiotic use.
By implementing these strategies and promoting responsible antibiotic use, we can combat the growing issue of antibiotic resistance and ensure the continued efficacy of Tetracycline in treating bacterial infections.
